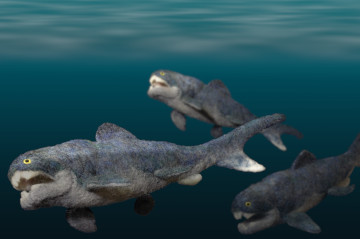
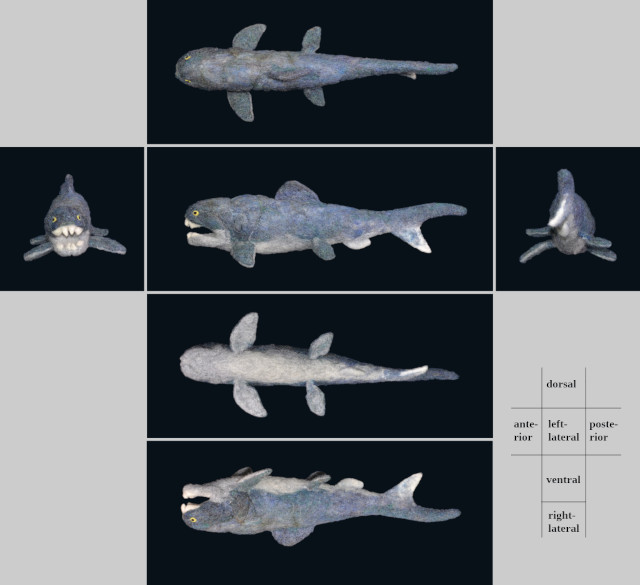
ダンクルオステウス Dunkleosteus terrelli
体長は従来4.5〜6mと考えられてきたが、生態形態学的なアプローチによるモデルからは最大8.79mと見積もられ、尾鰭も腹側の鰭構造が発達した異尾が考えられており、ダンクルオステウスは泳ぎがかなり上手だったことを示している 4)。
これらの特徴から、ダンクルオステウスは、素早い餌をも捕捉することができ、鱗や皮骨といった防御のための鎧も食い破るような、当時の生態系で、恐らく同じ板皮類の仲間も含め何でも食べてしまう捕食者の頂点に立っていたと考えられる 1), 2)。
参考文献・サイト:
- Anderson PSL, Westneat MW (2007) Feeding mechanics and bite force modelling of the skull of Dunkleosteus terrelli, an ancient apex predator. Biol. Lett. 3:76–79. (DOI:10.1098/rsbl.2006.0569)
- Anderson PSL, Westneat MW (2009) A biomechanical model of feeding kinematics for Dunkleosteus terrelli (Arthrodira, Placodermi). [abstract] Paleobiology 35(2) :251-269. (DOI:10.1666/08011.1)
- Carr RK (2010) Paleoecology of Dunkleosteus Terrelli (Placodermi: Arthrodira) The Cleveland Museum of Natural History PALEOECOLOGY OF DUNKLEOSTEUS TERRELLI (PLACODERMI: ARTHRODIRA). Kirtlamdia ( The Cleveland Museum of Natural History). No.57:36-45.
- Ferrón HG, Pérez CM, Botella H (2017) Ecomorphological inferences in early vertebrates: reconstructing Dunkleosteus terrelli (Arthrodira, Placodermi) caudal fin from palaeoecological data. PeerJ 5:e4081. (DOI: 10.7717/peerj.4081)
- Long J, Trinajstic K, Johanson Z (2009) Devonian arthrodire embryos and the origin of internal fertilization in vertebrates. [abstract] Nature 457:1124–1127. (DOI:10.1038/nature07732)




2020年3月 一部修正
2022年11月 一部修正